Global agricultural practices for successful cashew development
Practical Action
disadvantage of this method, as with all methods of layering, is the relatively small number of
layers that can be produced by one tree per year. It is estimated that from one tree, 80 to 120
successful layers can be obtained.
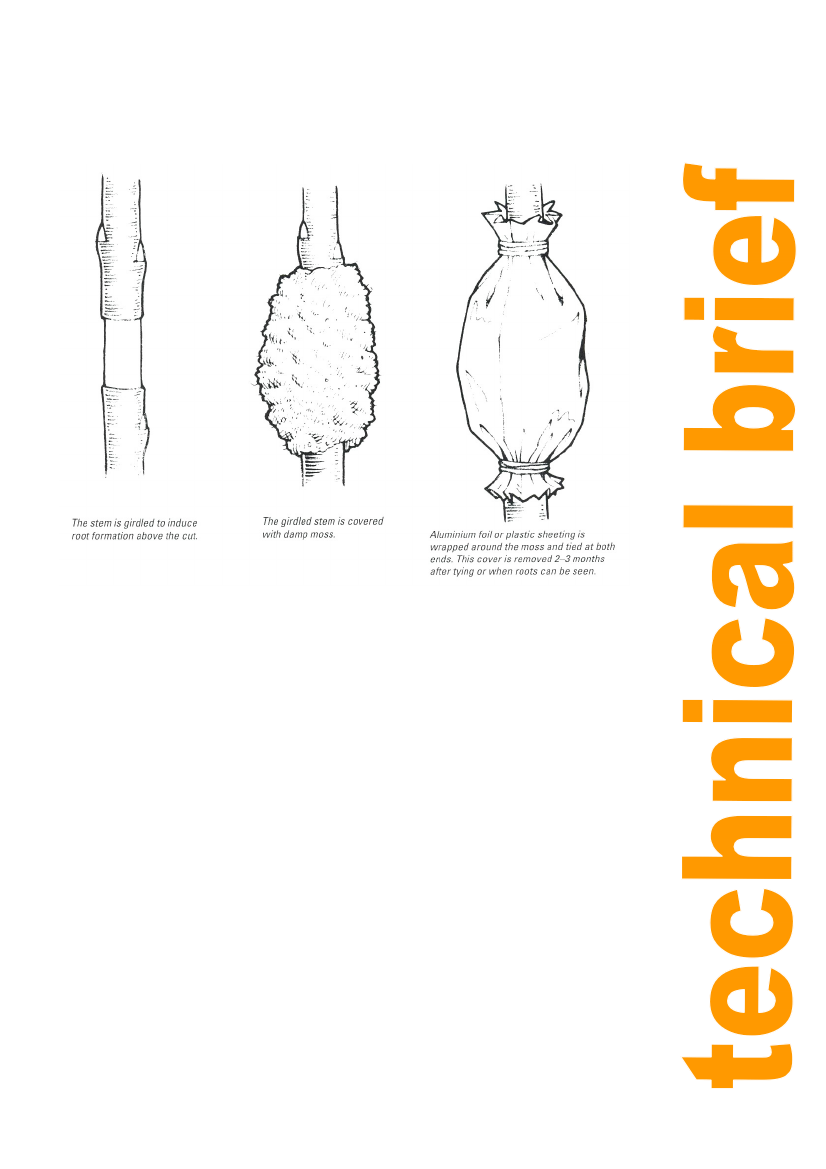
Figure 1: Air-layering.
A strip of bark about 0.5 cm wide is removed from either a year old branch or a pencil-thick
shoot (about 1 cm diameter) of the current season, at about 20-30 cm from the growing point.
The exposed wood is wrapped with twine to prevent the bark from growing over it during the
healing process and covered thickly with moist moss, wood shavings or sand. It is then
wrapped securely in a sheet of 100-150 gauge plastic and the ends are tied tightly to the
branch with twine (Figure 1).
After 20-30 days, callus is formed at the foot of the layer and 40-50 days later, small roots
emerge from the callus tissue. After approximately 75 days, there should be adequate root
formation (five or more well formed roots measuring 1.0-1.5 cm long) to separate the twig
from the tree. The part of the twig below the layer is cut about halfway through. One week
later, the cut is deepened and a few days later the layer can be removed and transplanted into
plastic bags or other containers and hardened off before planting. If the layer is separated
from the tree in one cut, the shock will be too great for it to survive. The whole process takes
about two and a half months.
Ground layering
The lowest branches of the cashew tree tend to trail on the ground at a distance of several
metres from the trunk. Where branches touch the ground, spontaneous rooting may occur.
Covering such branches with soil and keeping the area moist encourages rooting, a method
which has been used in India for a long time. However, such layers cannot be easily
transplanted to other places, and the shape of the material tends to produce low trees of
spreading habit. The number of layers that can be obtained in this way is also rather low.
3